An In-Depth Guide to Correcting Nasal Obstruction
Introduction
Septoplasty is a surgical procedure aimed at correcting a deviated nasal septum, which is a common cause of nasal obstruction and breathing difficulties. This comprehensive guide will explore the ins and outs of septoplasty, providing insights into who needs it, what the procedure involves, the recovery process, and the expected outcomes. Whether you are considering the surgery for yourself or are simply curious about its aspects, this article w

What is Septoplasty?
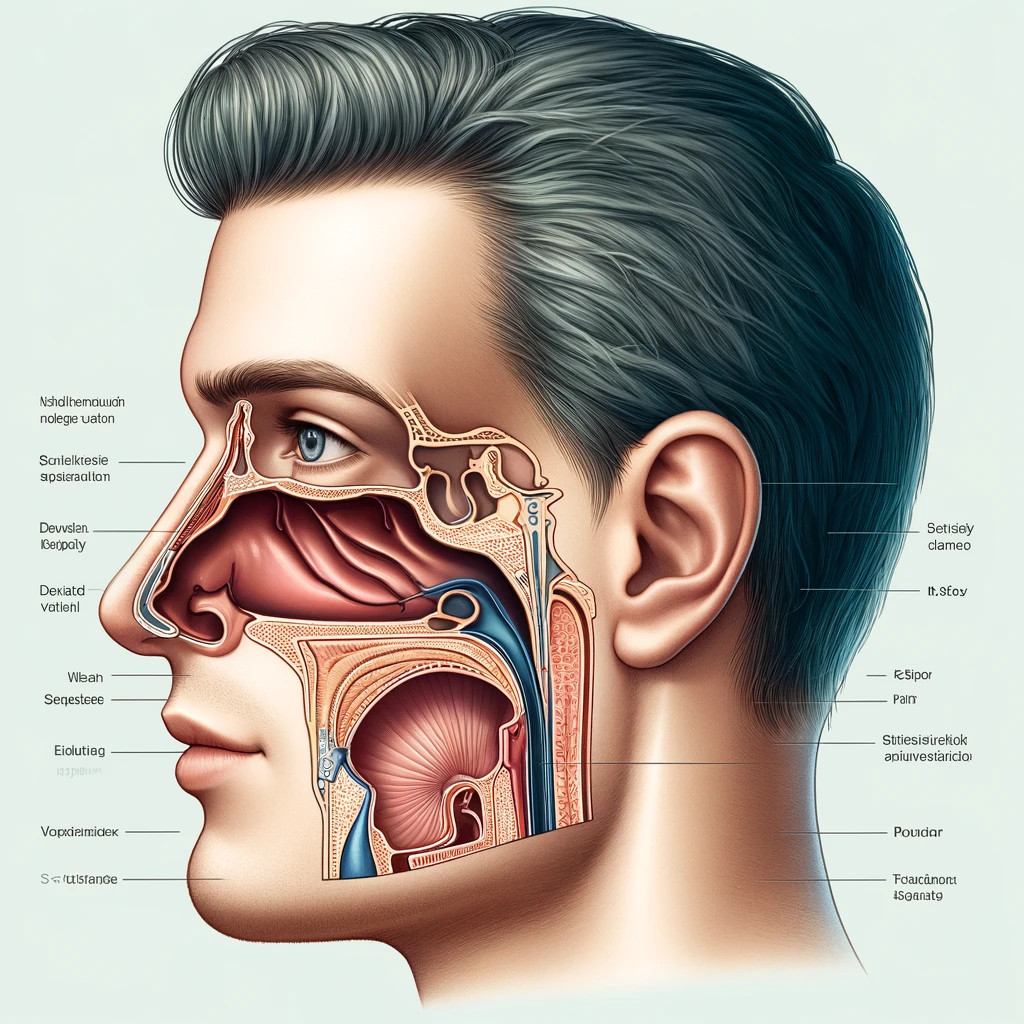
Septoplasty is a corrective surgical procedure that straightens the septum, the partition between the two nasal cavities. Ideally, the septum should sit at the center of the nose, allowing for even airflow. However, when it deviates, it can cause blockage of one or both nostrils, leading to difficulties in breathing, recurrent sinus infections, and other complications.
Indications for Septoplasty
- Chronic Nasal Congestion: The most common reason for septoplasty is persistent nasal blockage that affects one’s quality of life.
- Nasal Obstruction: Difficulty breathing through the nose due to septal deviation.
- Recurrent Sinusitis: Frequent sinus infections as a result of poor sinus drainage linked to a deviated septum.
- Snoring and Sleep Apnea: In some cases, a deviated septum can contribute to sleep disturbances and conditions like obstructive sleep apnea.
The Septoplasty Procedure
- Preoperative Assessment: Involves a thorough examination, including possibly a nasal endoscopy and imaging studies like a CT scan to assess the extent of the deviation.
- Anesthesia: Septoplasty is generally performed under general anesthesia, but in less extensive cases, local anesthesia with sedation may be used.
- The Surgery: The surgeon makes an incision inside the nose to access the septum. They then trim, reposition, and straighten the bent cartilage and bone. The incision is then closed with sutures, and if necessary, packing is placed inside the nose to support the new septal alignment.
- Duration: The procedure typically takes between 30 to 90 minutes, depending on the complexity of the deviation.
Recovery and Aftercare
- Initial Recovery: Patients might experience swelling, bruising, and mild discomfort immediately following surgery. Nasal packing, if used, is usually removed within a few days after the procedure.
- Long-term Care: Avoiding strenuous activities and potential injury to the nose during recovery is crucial. Follow-up visits are necessary to monitor the healing process.
- Expected Outcomes: Most patients notice significant improvements in breathing and a decrease in related symptoms post-recovery.
Risks and Complications
While septoplasty is generally safe, like all surgeries, it carries potential risks:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- An adverse reaction to anesthesia
- Septal Perforation: A rare complication where a hole remains in the septum post-surgery.
- Changes in Nose Shape: In some cases, there can be slight changes in the external appearance of the nose.
Choosing the Right Surgeon
Selecting a skilled and experienced ENT surgeon or a facial plastic surgeon who specializes in nasal surgeries is essential for ensuring a successful septoplasty with minimal complications.
Conclusion
Septoplasty is a proven solution for those suffering from complications related to a deviated septum. With the right preparation and care, it can significantly improve one’s quality of life by restoring optimal nasal function. As medical techniques continue to advance, septoplasty remains a safe, effective, and commonly recommended procedure for treating nasal obstructions.